1 Describe the general structure of an L-a amino acid at pH 70 and draw its structure. To amino acids and proteins.

Amino Acids Structure Classification Properties With Videos Examples
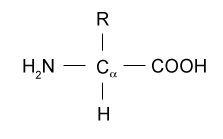
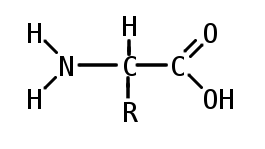
A carbon the alpha carbon A hydrogen atom H A Carboxyl group -COOH An Amino group -NH 2.

. 1 See answer Advertisement Advertisement. Biology questions and answers. Amino acids link together to form proteins.
Here is an example of deprotonating a protonated R group glutamic acid. Each amino acid has a central carbon called the α-carbon p0090 u0020 Explain the meaning of the terms pKa and pI as they apply to which four different groups are attached Fig. The base is attached to the 1 position of the ribose and the phosphate is attached to the 5 position.
How are amino acids linked together to form proteins. Amino acids are organic compounds containing amine -NH 2 and carboxyl -COOH functional groups along with side chain R group specific to each amino acids. The carbon atom of the carboxyl group has a free bond.
Structure of Amino Acids. Terms in this set 16. A polypeptide folds into a 3D structure called a protein.
Note that this is the WRONG structure at a neutral pH. At the center of each amino acid is a carbon called the and attached to it are four groups a hydrogen a carboxylic acid group an amine group and an R-group sometimes referred to as a variable group or side chain. All amino acids found in proteins have this basic structure differing only in the structure of the R-group or the side chain.
Each amino acid has the same fundamental structure which consists of a central carbon atom also known as the alpha α carbon bonded to an amino group NH 2 a carboxyl group COOH and to a hydrogen atom. All amino acids have the same basic structure shown in Figure 21. This carbon is covalently bonded to four different groups.
Describe the basic general structure of an l-a-amino acid. -All amino acids contain an alpha-amino group and also an alpha-carboxyl group. Any carbon atom other than that of the carboxyl COOH group may be linked to the amino group NH 2.
The R can represent one of 20 different side chains. An amino group a carboxyl group a hydrogen atom and a variable group symbolised by R. General structure of amino acid Twenty different amino acids are commonly found in proteins.
20 rows Amino acids are molecules used to build proteins. Properties of Amino Acids They are crystalline colourless compounds. 2 Using the 5 categories into which the 20 naturally occurring amino acids are classified draw the structure of.
Here is the structures at increasing pHs for a generic amino acid. Two types of pentose are found in nucleotides deoxyribose found in DNA and ribose found in RNA. Click card to see definition.
Chemistry questions and answers. In the centre of the amino acid is an assymetric carbon atom called the alpha carbon. First week only 499.
Structure of an Amino Acid Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins. This is usually a trap answer on tests. Although all these have varied structures the basic structure of amino acid remains uniform.
Tap card to see definition. -Side chain is distinctive for each amino acid. Structure of Amino Acids Amino acids are the basic components of proteins.
An amino acid consists of a central or alpha carbon atom attached to an amino group NH2 a carboxylic acid group COOH a hydrogen atom and a variable side group called the R group. The basic structure of an amino acid an amino acid consists of one central carbon. -The alpha-carboxyl group is Carbon 2 the carboxyl carbon is Carbon 1.
Describe the general structure and stereochemistry of amino acids. If you start at a high pH and decrease it read the structures from right to left. Ah hydrogen carb oxalic acid group in the Mean group and another group thats different from all these usually different to say sometimes called the our group or sometimes called the side chain.
Start your trial now. Generally amino acids have the following structural properties. A water molecule is removed by releasing an OH from carboxyl group of one amino acid and hydrogen from the amino group of another amino acid.
The R group also known as a side chain is different for each. Describe the various levels of protein structure primary secondary tertiary and quaternary. The other two groups connected to the central carbon is the R-group which determines the identity of the amino acid for example alanines R-group is just a methyl group and a simple hydrogen atom.
As we mentioned there are 20 common amino acids present in proteins. Amino acids are the monomers that comprise polypeptides polypeptides being the polymers. All amino acids contain a carbon atom in the middle of the molecule the alpha-carbon This atom is surrounded by three chemical groups.
1Describe the basic structure of an amino acid. All amino acids have a central carbon atom. Its which are bonded.
An amino acid contains a central tetrahedral carbon called the alpha carbon. All amino acids found in protein have a basic structure which differ only in the structure of the R-group or the side chain. The α carbon carboxylic acid and amino groups are common to all amino acids so the R.
Connected to it on either side is a carboxylate group and an amino group. Amino acids link together to form proteins. When a polynucleotide is formed the 5 phosphate of the incoming nucleotide attaches to the 3 hydroxyl group at the end of the growing chain.
Biology Middle School answered Describe the structure of amino acids including what makes amino acids different from each other. Describe the basic general structure of an l-a-amino acidand draw its structure. They are the monomeric unit or building blocks of proteins.
Ah hydrogen carb oxalic acid group in the Mean group and another group thats different from all these usually different to say sometimes called the our group or sometimes called the side chain. The simplest and smallest amino acid is found in proteins is glycerin for which the R-group is a H hydrogen. There are 20 different amino acids and they all share the same general structure.
U0030 Describe the elements of the primary secondary tertiary a basic amino group NH2 u0060 and quaternary structure of. Scientists use the name amino acid because these acids contain both amino group and carboxyl-acid-group in their basic structure. The simplest and smallest amino acid found in proteins is glycine for which the R-group is a hydrogen H.
One is an amine group -NH 2 The second one is a carboxyl group -OOOH The third group is denoted by R. Solution for Describe the basic general structure of an l-a-amino acidand draw its structure. The basic structure of an amino acid an amino acid consists of one central carbon.
Its which are bonded. The amino acids in a protein are bonded to each other with peptide bonds - hence the term for a polymer of amino acids is a polypeptide. Organic substances containing both amino and carboxylic groups are known as amino acids.
Basic Structure of an Amino Acid. What is the pka range for the carboxylic acid group and the amine group in amino acid.
0 Comments